Summary
-
Fundamental theory of VSAT communications for all VSAT technicians and engineers. Includes advanced interactive graphical simulations.
Description
GVF520, the second in a series of three online courses leading to Advanced Satcom Professional Certification, provides the student with a thorough understanding of the fundamental theories of satellite communications. This knowledge is essential for every skilled and effective satellite ground equipment terminal field technician.
Audience:
The course is appropriate for all installers and field technicians who may be responsible for activating any type of VSAT terminal, as well as engineers and technicians desiring a technical introduction to two-way satellite communications.
Delivery:
Animated & interactive HTML5, self-paced, on-line format. Requirements: internet access while studying the course material (high speed preferred ); current browser with JavaScript enabled; permission to access SatProf server and learning system websites; mouse.
Tests:
Each lesson contains a mandatory quiz and simulator-based skills assessments. All pages must be viewed and all quizzes and simulator tests must be passed in order to satisfactorily complete the course.Lessons
17 lessons
- Course introduction, including review of Certification requirements.
- Satellite communications overview, including spacecraft, transponders, and launch vehicles.
- Orbits, with interactive simulator-based orbital mechanics experimenters and 3-D constellation animations.
- Footprints, explaining EIRP, G/T, contours, and their relationships to dish size.
- Waves, including interactive experimenters for amplitude and frequency; latency; satcom bands.
- Gains, losses, and levels, covering fundamentals of dB and level calculations, with interactive animated exercises.
- Signals, noise, and spectrums, including real-time spectrum simulation of bandwidth, noise, and C/N.
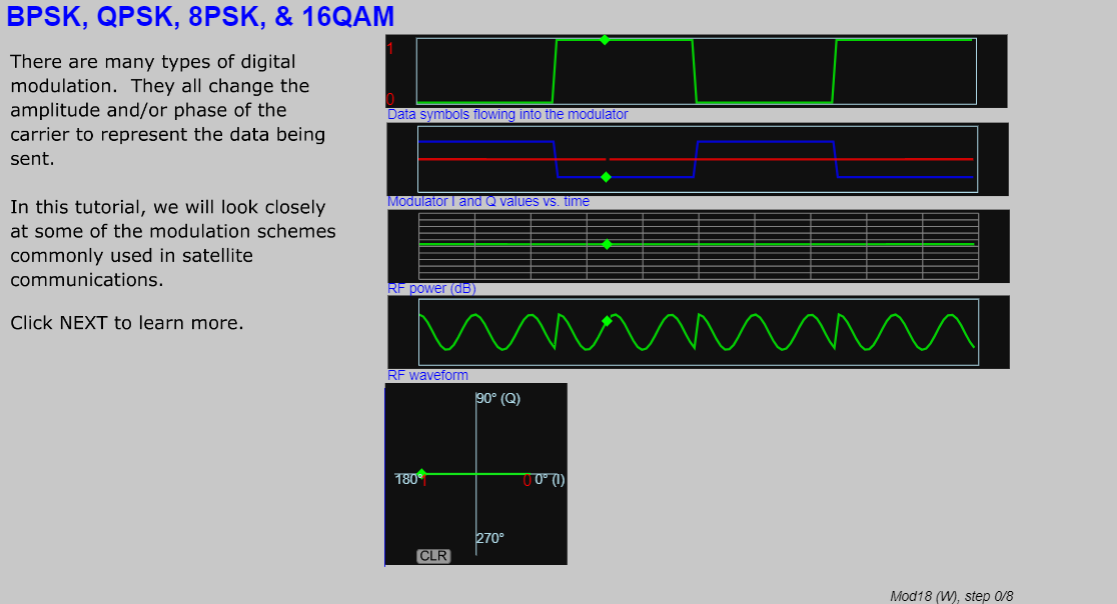
- Modulation, with animated explanations of QPSK, 8PSK, etc, forward error correction, and bit error rate.
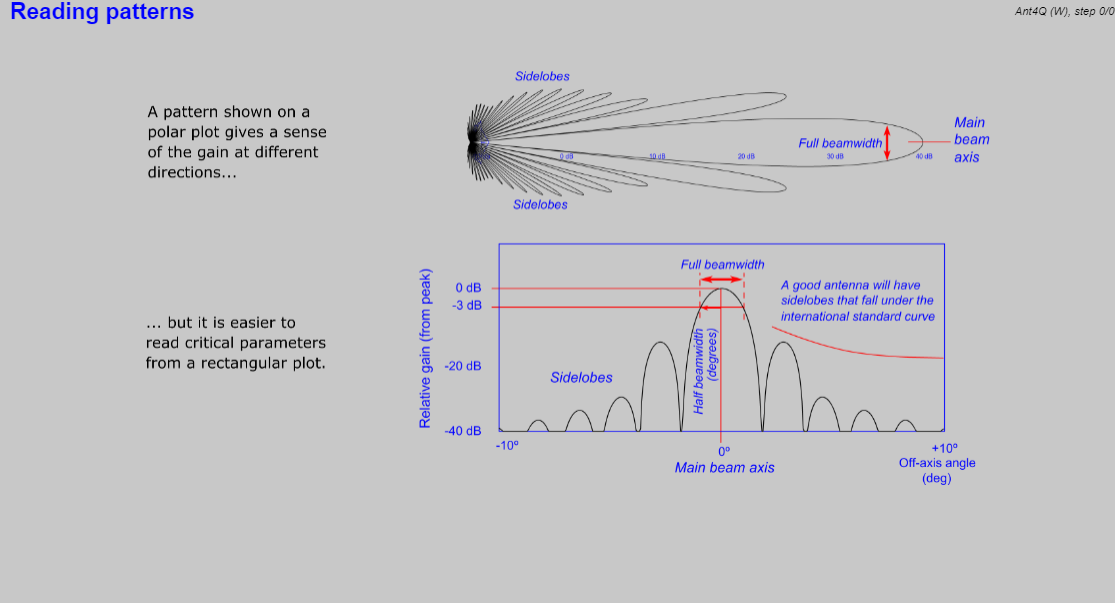
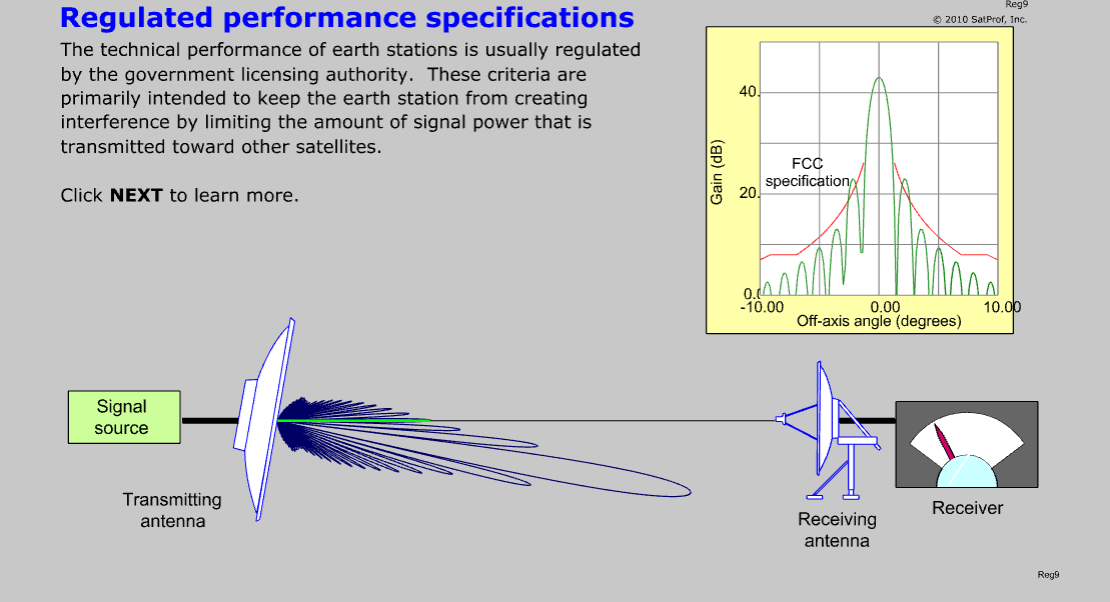
- Antennas, including sidelobes, patterns, and gain, with interactive experimenters.
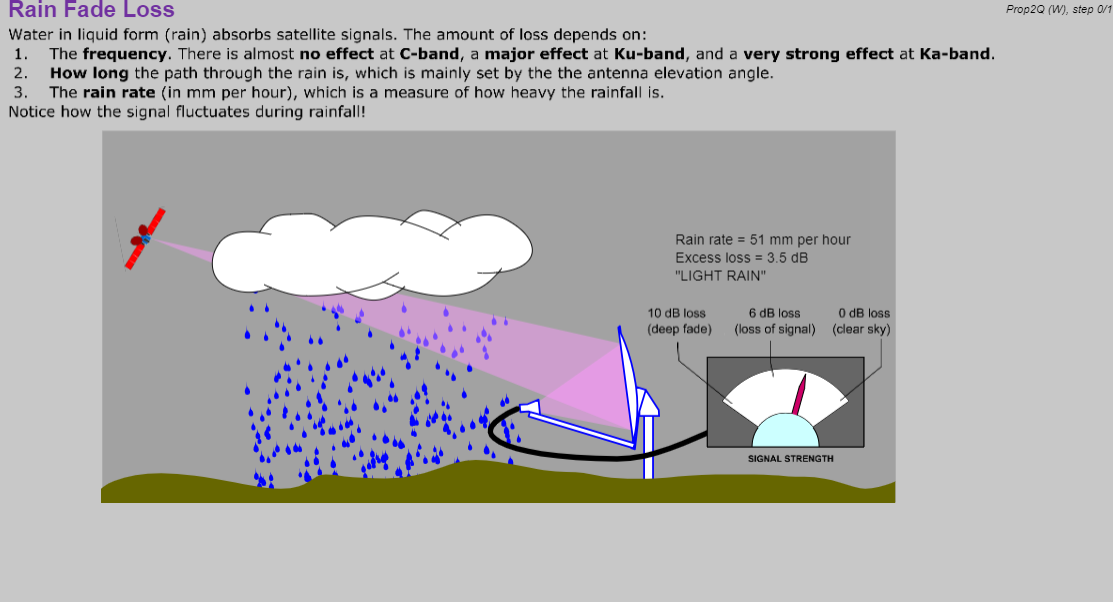
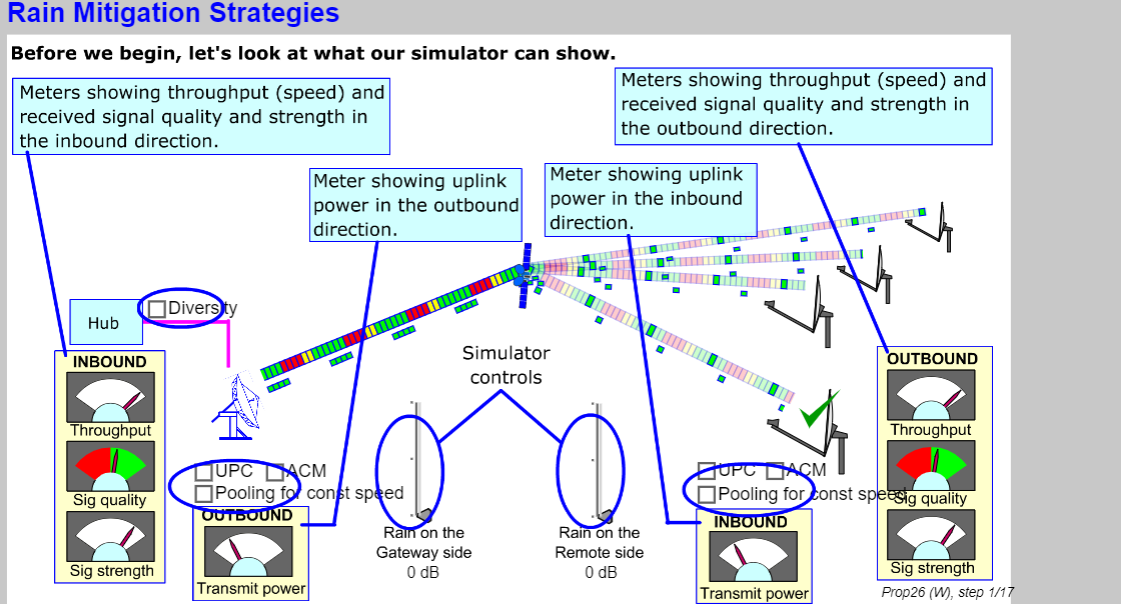
- Propagation, including rain fade, blockage, snow/ice effects, and animated solar transit outage demonstration.
- Satellite links, with breakdown of how a link budget concepts, link margins, and availability.
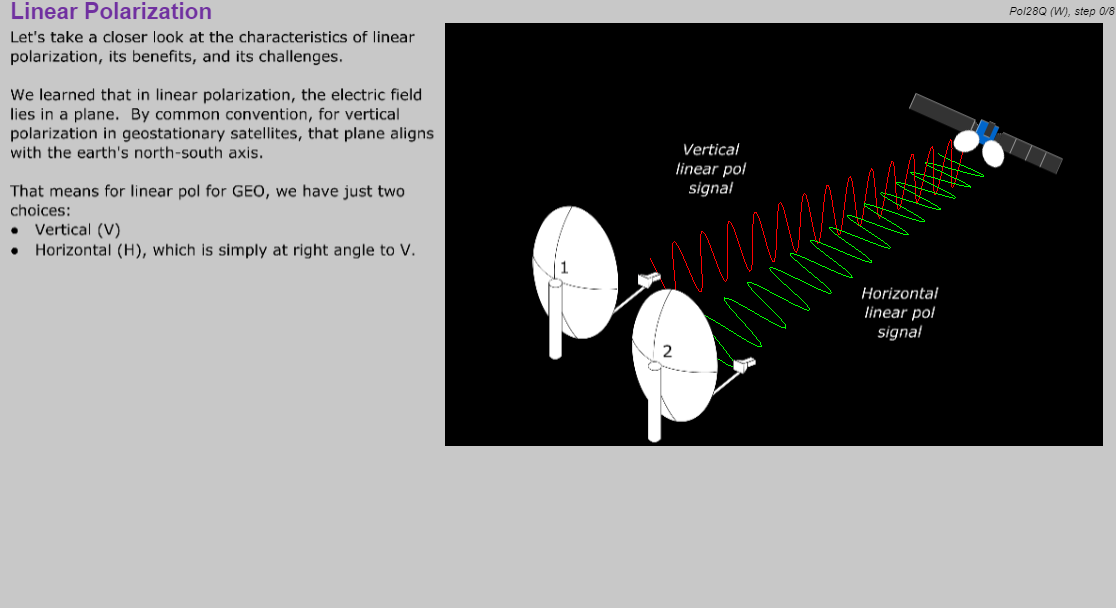
- Polarization, with 3-D interactive animations of linear and circular pol waves, feed systems, and XPD.
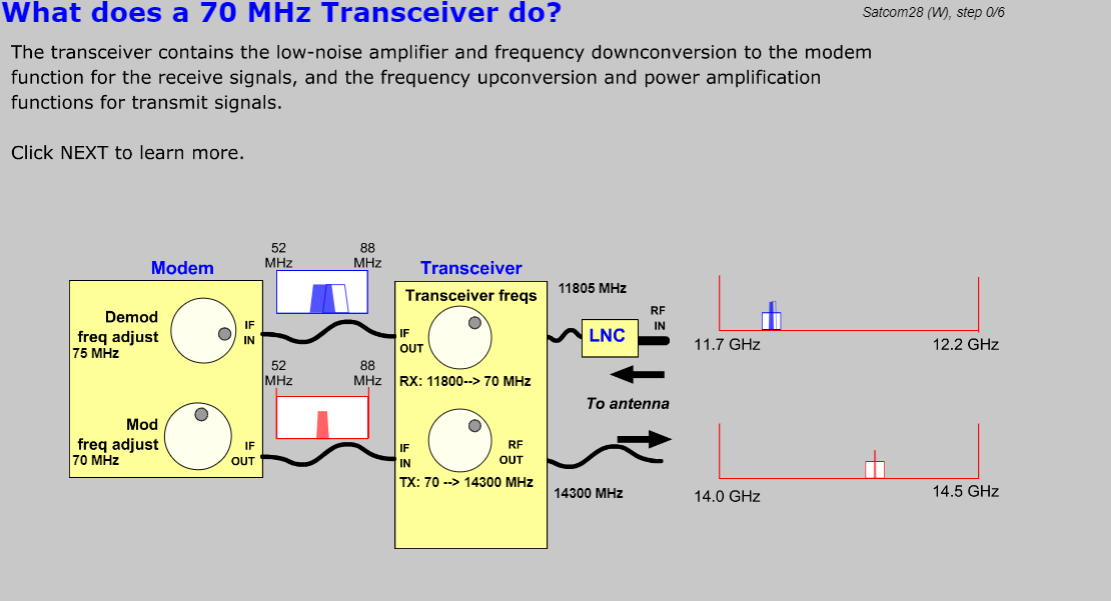
- Earth station and VSAT equipment, including expanded discussion of components found in larger earth stations.
- Access methods, with animated diagrams of SCPC, TDMA, TDM, DAMA, and DVB.
- Mobile VSAT overview, including 3-D illustrations of auto-deploy and marine stabilized antennas.
- Considering VSAT networks, with discussion of cost, regulatory, safety, and installation issues.
- Comparing satellites, including review of satellite advantages and alternatives for specific services.
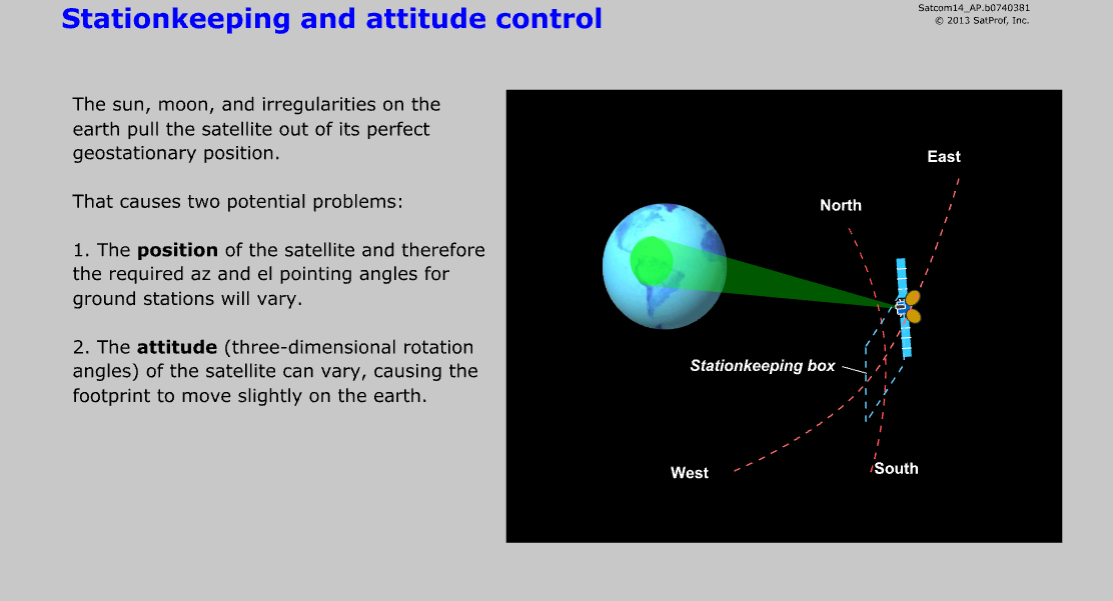


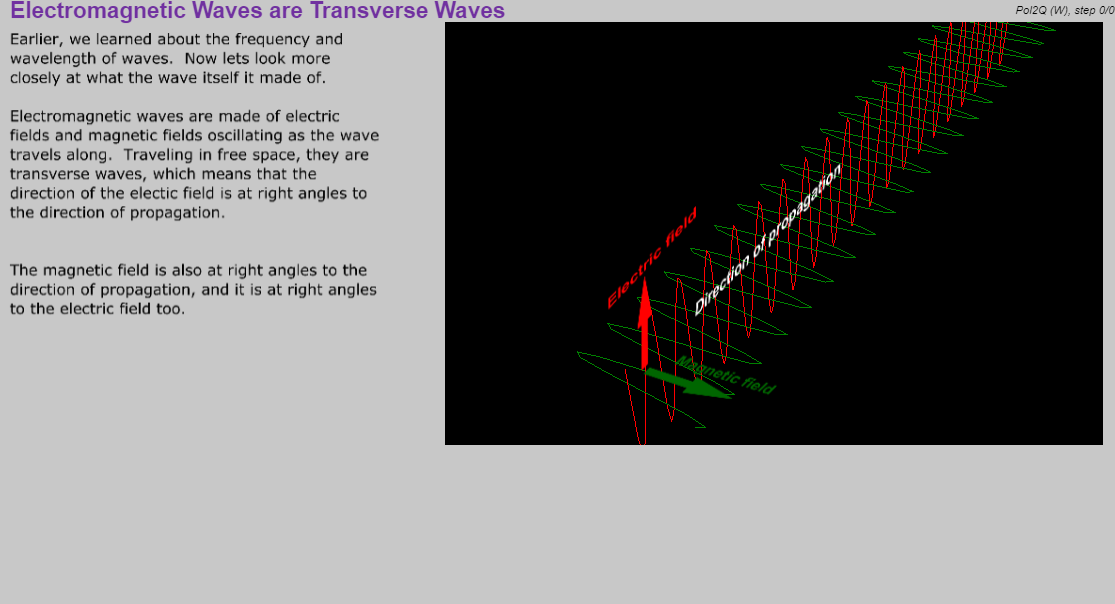
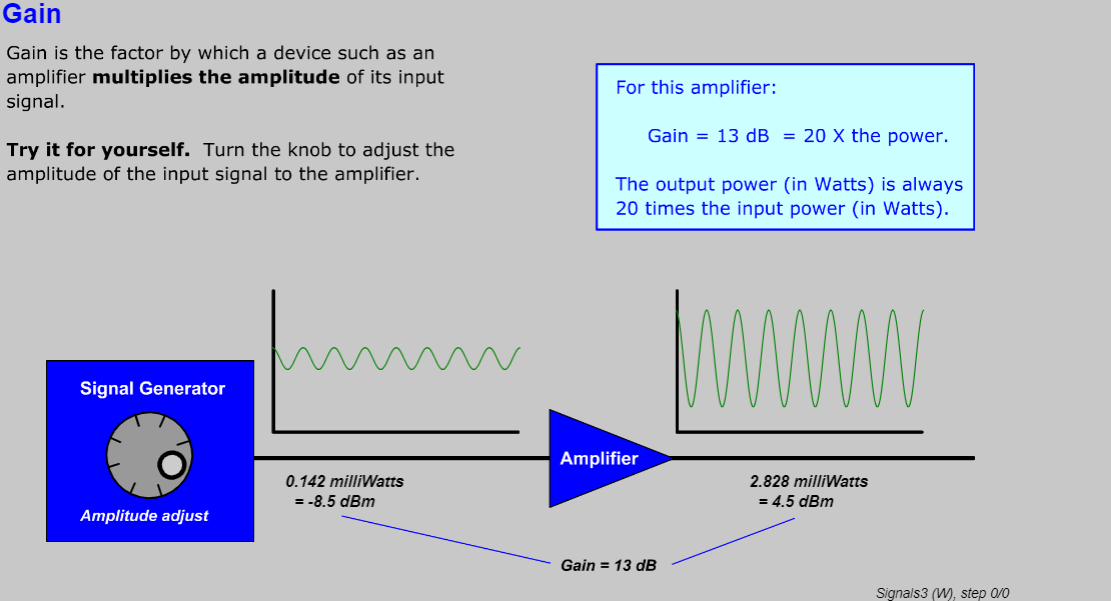
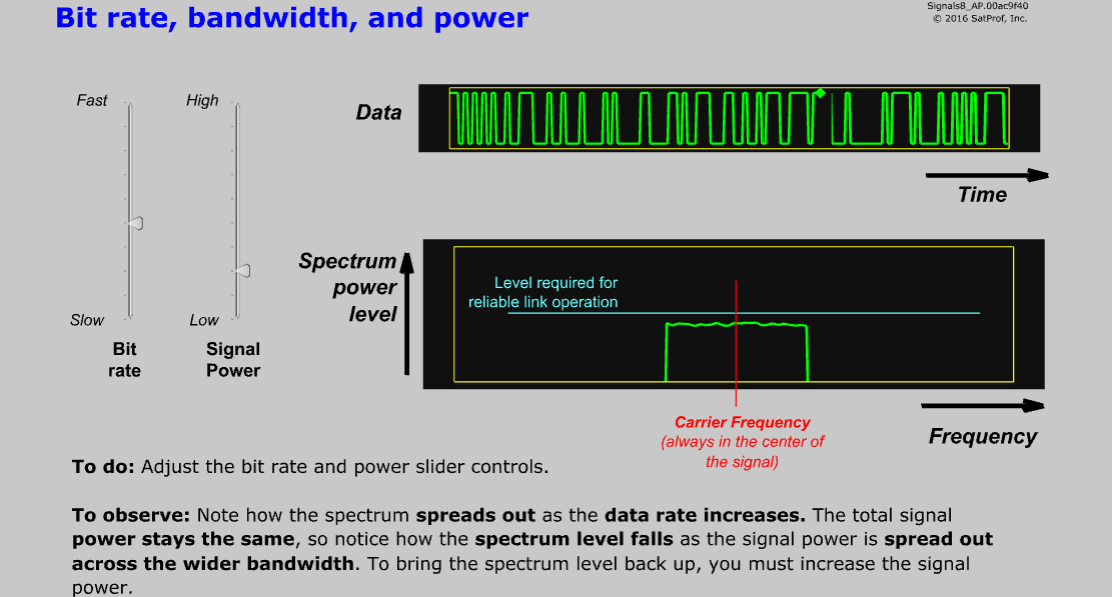

Learning Objectives
- General understanding satellite communications theory at a technician level;
- Compare satellite, wireless, wired, and fiber communications and their preferred applications;
- Describe spacecraft physical size, payloads, transponders, antennas, lifetime;
- Describe typical launch vehicles;
- Compare LEO, MEO, and GEO orbits;
- Identify GEO arc as viewed from the earth and space;
- Describe the concepts of links, link budgets, and how they are affected by dish size;
- Define qualitatively EIRP, G/T, footprints, and contours ;
- Describe the main properties of microwaves and how signals are affected by blockage;
- List the frequencies bands used for satellite communications;
- Define rain fade loss, rain zones, availability;
- Explain solar outages;
- Describe the operation of a satellite transponder.
- Compare co- and cross-pol transponders.
- Define linear polarization, polarization angle, cross-pol alignment and interference, pol re-use, and circular polarization.
- Identify the main hardware components in a VSAT and a larger earth station.
- Define the functions of the antenna, LNB, TRF, BUC, IFL, OMT, waveguide, and modem.
- Compare the main types of antennas used for earth stations.
- Describe sidelobes and beamwidth.
- Describe the relationships between antenna size, frequency band, beamwidth, and gain.
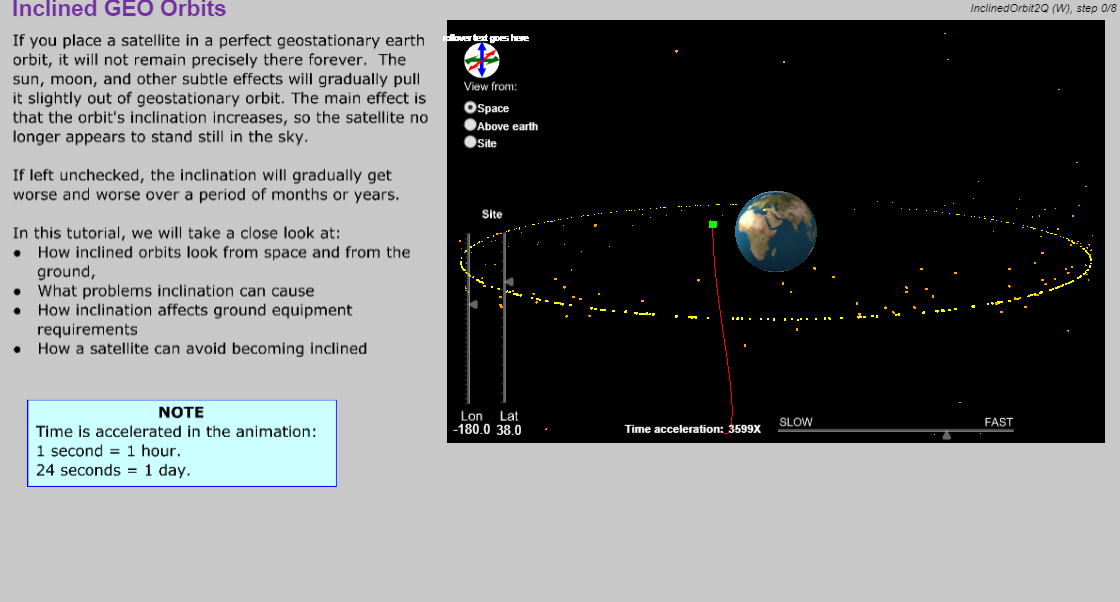
- Describe the how inclined orbit satellites affect ground antennas.
- Define amplitude, frequency, decibels, gain, EIRP, spectrum, symbol rate, bandwidth, noise, power, C/N, and Eb/No.
- Define modulation and demodulation. Describe and compare BPSK, QPSK, and 8PSK.
- Define and describe SCPC, TDM, TDMA, MF-TDMA, DVB, DVB-RCS, star, and mesh networks.
- Describe the functions of a LAN, Ethernet, IP address, subnet, gateway/router address, DNS, DHCP, NAT.
- Define the functions of nonroutable addresses, ping, and tracert.
- Identify and compare auto-point and stabilized antennas.
- Describe the process of automatic acquisition in an auto-point antenna.